-
Cell Types: Monocrystalline Silicon Cells
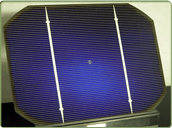 Made using cells saw-cut from a single cylindrical crystal of silicon, they are effectively a slice from a crystal. This is the most efficient of the photovoltaic (PV) technologies. The principle advantage of monocrystalline cells are their high efficiencies, typically around 15%, although the manufacturing process required to produce monocrystalline silicon is complicated, resulting in slightly higher costs than other technologies. In appearance, it will have a smooth texture and you will be able to see the thickness of the slice. They are also rigid and must be mounted in a rigid frame top protect them.
Made using cells saw-cut from a single cylindrical crystal of silicon, they are effectively a slice from a crystal. This is the most efficient of the photovoltaic (PV) technologies. The principle advantage of monocrystalline cells are their high efficiencies, typically around 15%, although the manufacturing process required to produce monocrystalline silicon is complicated, resulting in slightly higher costs than other technologies. In appearance, it will have a smooth texture and you will be able to see the thickness of the slice. They are also rigid and must be mounted in a rigid frame top protect them.
-
Cell Types: Polycrystalline or Multicrystalline Silicon Cells
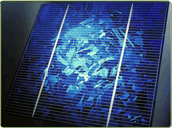 Made from cells cut from an ingot of melted and recrystallised silicon. In the manufacturing process, molten silicon is cast into ingots of polycrystalline silicon, these ingots are then saw-cut into very thin wafers and assembled into complete cells. Multicrystalline cells are cheaper to produce than monocrystalline ones, due to the simpler manufacturing process. However, they tend to be slightly less efficient, with average efficiencies of around 12%. They have a speckled crystal reflective appearance, and again need to be mounted in a rigid frame.
Made from cells cut from an ingot of melted and recrystallised silicon. In the manufacturing process, molten silicon is cast into ingots of polycrystalline silicon, these ingots are then saw-cut into very thin wafers and assembled into complete cells. Multicrystalline cells are cheaper to produce than monocrystalline ones, due to the simpler manufacturing process. However, they tend to be slightly less efficient, with average efficiencies of around 12%. They have a speckled crystal reflective appearance, and again need to be mounted in a rigid frame.
-
Cell Types: Amorphous Silicon
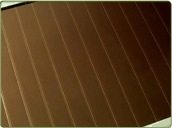 Amorphous silicon cells are composed of silicon atoms in a thin homogenous layer rather than a crystal structure. Amorphous silicon absorbs light more effectively than crystalline silicon, so the cells can be thinner. For this reason, amorphous silicon is also known as a "thin film" PV technology. Amorphous silicon can be deposited on a wide range of substrates, both rigid and flexible, which makes it ideal for curved surfaces and "fold-away" modules. Amorphous cells are, however, less efficient than crystalline based cells, with typical efficiencies of around 6%, but they are easier and therefore cheaper to produce. Their low cost makes them ideally suited for many applications where high efficiency is not required and low cost is important. One characteristic of amorphous solar cels is that their power output reduces over time, particularly during the first few months, after which time they are basically stable. The quoted output of an amorphous panel should be that produced after this stabilization.
Amorphous silicon cells are composed of silicon atoms in a thin homogenous layer rather than a crystal structure. Amorphous silicon absorbs light more effectively than crystalline silicon, so the cells can be thinner. For this reason, amorphous silicon is also known as a "thin film" PV technology. Amorphous silicon can be deposited on a wide range of substrates, both rigid and flexible, which makes it ideal for curved surfaces and "fold-away" modules. Amorphous cells are, however, less efficient than crystalline based cells, with typical efficiencies of around 6%, but they are easier and therefore cheaper to produce. Their low cost makes them ideally suited for many applications where high efficiency is not required and low cost is important. One characteristic of amorphous solar cels is that their power output reduces over time, particularly during the first few months, after which time they are basically stable. The quoted output of an amorphous panel should be that produced after this stabilization.
-
Cell Types: Efficiency Table
-
Solar cells efficiency vary depending on the materials originally there were made of. The following table summarizes the efficiency:
- Material
- Cell Efficiency
- • Monocrystalline
- • Polycrystalline
- • Thin-film
- • Amorphous
- • Polymer
- • 18%
- • 13-15%
- • 10-12%
- • 5-7%
- • 5%

